Manufacturing of wind turbines is a job opportunity
Wind turbine manufacturing jobs include a variety of tasks that require specialized knowledge and skills. These jobs include assembly of towers, blade epoxies, and gears. Many wind turbine manufacturers also work with third-party suppliers to produce various components. Wind turbine components are large and need to be transported quickly and efficiently. Teams of logisticians or rail freight drivers are needed by companies to complete this task.
Most jobs in the manufacturing of wind turbines require a bachelor's or master's degree. Generally, jobs in wind turbine manufacturing require engineering and environmental engineering concentrations. Entry-level engineers need to have advanced computer skills and previous experience in addition to a degree. They usually work with more experienced employees to ensure quality control and accuracy. They may also be asked to work on more complex projects.
There are many steps involved in manufacturing wind turbines
The main component of a wind turbine is the blades. Each blade has two faces connected by integral shear Webs. The blades are supported by a box spar and shell fairings. These structures can withstand both edgewise and flapwise loads. The spar resists edgewise bending from wind pressure and gravitational forces. These forces can be resisted by the blades.
The blades are made from a variety of materials. While fiberglass is the most popular material used for commercial wind turbine blades, aluminum and lightweight woods are also used. The blades then get covered with foil and are connected to tubes that pump resin.
Competitors in wind turbine manufacturing
While Chinese turbine manufacturers are becoming a more prominent player in the global wind industry's overall structure, they still have a long way to go before they become the dominant force. Chinese turbine manufacturers have struggled to dethrone incumbents in developed markets. Despite this, they may be poised to eventually increase their overseas activities if they invest in local manufacturing capabilities.
Although large turbine manufacturers are increasingly outsourcing components, many individuals are still choosing to build the parts themselves. This has both advantages and disadvantages. Vestas, a Colorado-based company that manufactures wind turbines towers for US third-party projects, has adopted this strategy. The agreement gives the tower plant access to up to 25 per cent of its production capabilities and supports 100 local workers. But, this approach comes with a drawback: weak quality control. Some components from offshore suppliers have had problems in the past. These include gearbox failures, blade cracking, and gearbox failures. Some foundations offshore are made from low quality steel.
Wind turbine manufacturing poses safety and health risks
Wind turbine manufacturing is a hazardous industry. Safety and health are paramount. Workers are often exposed to a number of hazards that could lead to long-term damage or even fatalities. Fortunately, there are ways to reduce the risk, including proper training and routine inspections. Here are some tips that will keep employees safe in a wind turbine manufacturing plant.

Exposure to dangerous gases, vapors and dust is one of the greatest hazards in the manufacturing of wind turbine blades. To reduce this risk, workers must wear respirators. They also need to be trained on how to use them. Good training is key to ensuring that workers are protected from the elements.
FAQ
What are the products and services of logistics?
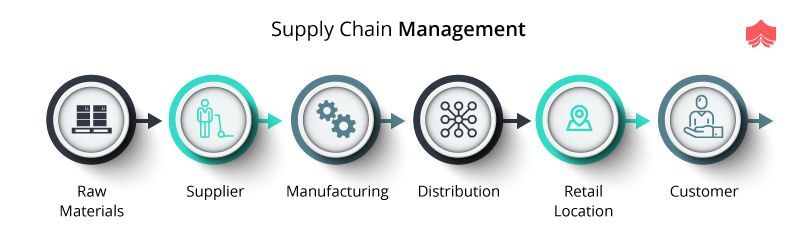
Logistics refers to all activities that involve moving goods from A to B.
They encompass all aspects transport, including packaging and loading, transporting, storage, unloading.
Logisticians make sure that the right product arrives at the right place at the correct time and in safe conditions. Logisticians assist companies in managing their supply chains by providing information such as demand forecasts, stock levels and production schedules.
They also keep track of shipments in transit, monitor quality standards, perform inventories and order replenishment, coordinate with suppliers and vendors, and provide support services for sales and marketing.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
What is the best way to learn about manufacturing?
Experience is the best way for you to learn about manufacturing. However, if that's not possible, you can always read books or watch educational videos.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics.
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters make up the acronym:
-
Responsible - to ensure that all actions are within the legal requirements and are not detrimental to others.
-
Reliable – have faith in your ability and capability to keep promises.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - Consider all aspects of operations, including environmental impact and cost effectiveness.
-
Respectful - show respect and treat others fairly and fairly
-
Responsive - Look for ways to save time and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable - provide customers with value-added services.
Why is logistics important for manufacturing?
Logistics are essential to any business. Logistics can help you achieve amazing results by helping to manage product flow from raw materials to finished products.
Logistics also play a major role in reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Why should you automate your warehouse?
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. The rise of e-commerce has led to increased demand for faster delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses must adapt quickly to meet changing customer needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
Increases efficiency of workers
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
Ensures quality products are delivered on time
-
Removes human error
-
It ensures compliance with regulations
How can overproduction in manufacturing be reduced?
In order to reduce excess production, you need to develop better inventory management methods. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
Kanban systems are one way to achieve this. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. Kanban systems allow work items to move through different states until they reach their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
If work is moving from one stage to the other, then the current task can be completed and moved on to the next. However, if a task is still at the beginning stages, it will remain so until it reaches the end of the process.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. With a Kanban board, managers can see exactly how much work is being done at any given moment. This data allows them adjust their workflow based upon real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate waste from every step of the production cycle. Anything that doesn't add value to the product is considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Packaging not required
-
Excess materials
By implementing these ideas, manufacturers can improve efficiency and cut costs.
Statistics
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma refers to "the application and control of statistical processes (SPC) techniques in order to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department developed it at their Tokyo plant in Japan in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. Six Sigma's main objective is to reduce variations from the production average. It is possible to measure the performance of your product against an average and find the percentage of time that it differs from the norm. If you notice a large deviation, then it is time to fix it.
The first step toward implementing Six Sigma is understanding how variability works in your business. Once you understand this, you can then identify the causes of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations occur when people do mistakes. Symmetrical variations are caused due to factors beyond the process. You could consider random variations if some widgets fall off the assembly lines. If however, you notice that each time you assemble a widget it falls apart in exactly the same spot, that is a problem.
Once you identify the problem areas, it is time to create solutions. The solution could involve changing how you do things, or redesigning your entire process. After implementing the new changes, you should test them again to see if they worked. If they don’t work, you’ll need to go back and rework the plan.