
No matter your experience level, the demand for jobs in additive manufacturing is growing. McKinsey predicts that additive manufacturing will have a $100 billion-250 billion economic impact by 2025. Those interested in the field should consider educational and career paths that will prepare them for the future.
One of the most common careers in additive manufacturing is that of material scientist. These people are responsible for evaluating the properties of materials and inventing new ones. These individuals can also help develop post-processing methods and conduct research into the future 3D printing materials.
Although there are many kinds of material scientists, the median salary for these individuals hovers around $150,000. Many jobs involve research, development, or testing the mechanical property of materials. Some jobs focus more on developing new applications for additive production.

This industry has experienced a lot growth in the past year. AT Kearney says that in the US, additive manufacturing could generate up to five millions skilled jobs within a decade. The technology is being adopted by more companies, which means that engineers, business professionals, marketing and sales professionals are needed to support them and their products.
You will typically need to have several years experience, a bachelor’s degree, and knowledge about the software used in additive manufacturing. But, primary qualifications can vary from one job to the next. Not only do you need a solid educational background but also communication skills and data analysis.
R&D are the most popular jobs in additive production. In fact, 58% employers anticipate hiring R&D positions in the next 12 months. These positions include designers, who create digital models of 3D objects, and industrialists, who are responsible for developing additive manufacturing processes.
The next most in-demand jobs are those that involve sales. Typically, these positions require a bachelor's degree or higher, but some employers will prefer candidates with advanced degrees. In addition, sales personnel are needed for many different industries, including automobiles, aerospace, and food.
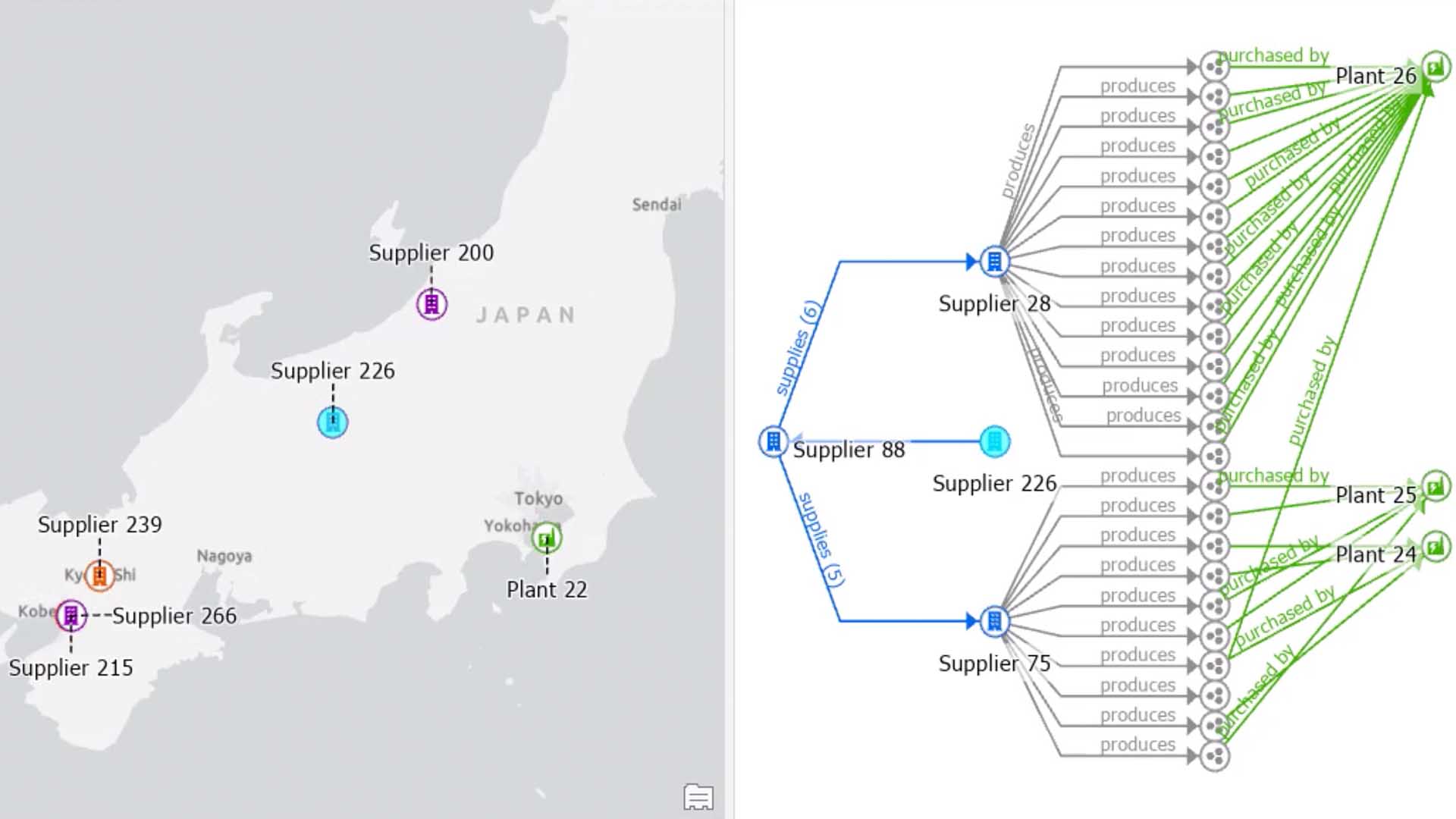
Software is another area of employment that is experiencing rapid growth. Companies are using technology to create cross-platform software. This is a non-linear career path. Employers are looking for applicants who have mental flexibility, problem solving skills that require complex problem solving, and creativity. Professionals can land this job by developing these skills, and then demonstrating them to potential employers.
Finally, many job postings require a degree in computer science. While this is not the most common educational path, it can help professionals build the skills necessary for a career in additive manufacturing.
Although the future is uncertain for additive manufacturing, it is important to stay on top of the industry's growth. This will help you decide whether this is the right field for you. Joblist can help you search for and apply to job opportunities in this field if you're interested.
FAQ
How can I learn about manufacturing?
Practical experience is the best way of learning about manufacturing. If that is not possible, you could always read books or view educational videos.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. They must invest heavily in technology to do this. Automation warehouses can bring many benefits. These are some of the benefits that automation can bring to warehouses:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale more easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
Ensures quality products are delivered on time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
Assure compliance with regulations
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym 7R's for Logistics stands to represent the seven basic principles in logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The acronym consists of the following letters:
-
Responsible - to ensure that all actions are within the legal requirements and are not detrimental to others.
-
Reliable - have confidence in the ability to deliver on commitments made.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic – consider all aspects of operations, from cost-effectiveness to environmental impact.
-
Respectful - treat people fairly and equitably.
-
Reliable - Find ways to save money and increase your productivity.
-
Recognizable: Provide customers with value-added service
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to use lean manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management system that aims at increasing efficiency and reducing waste. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five basic principles of Lean Manufacturing are included in lean manufacturing
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. In fact, some economists believe that lean manufacturing will be an important factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is becoming a popular practice in automotive. It has many advantages. These benefits include increased customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels and lower operating costs.
Any aspect of an enterprise can benefit from Lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. If a part is required to be repaired on the assembly line, it should not be scrapped. This is also true for finished products that require minor repairs before shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI),: Continuous improvement aims improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by continuously identifying issues and making changes to reduce waste. Continuous improvement involves continuous improvement of processes and people as well as tools.